Category: Tutorials
-
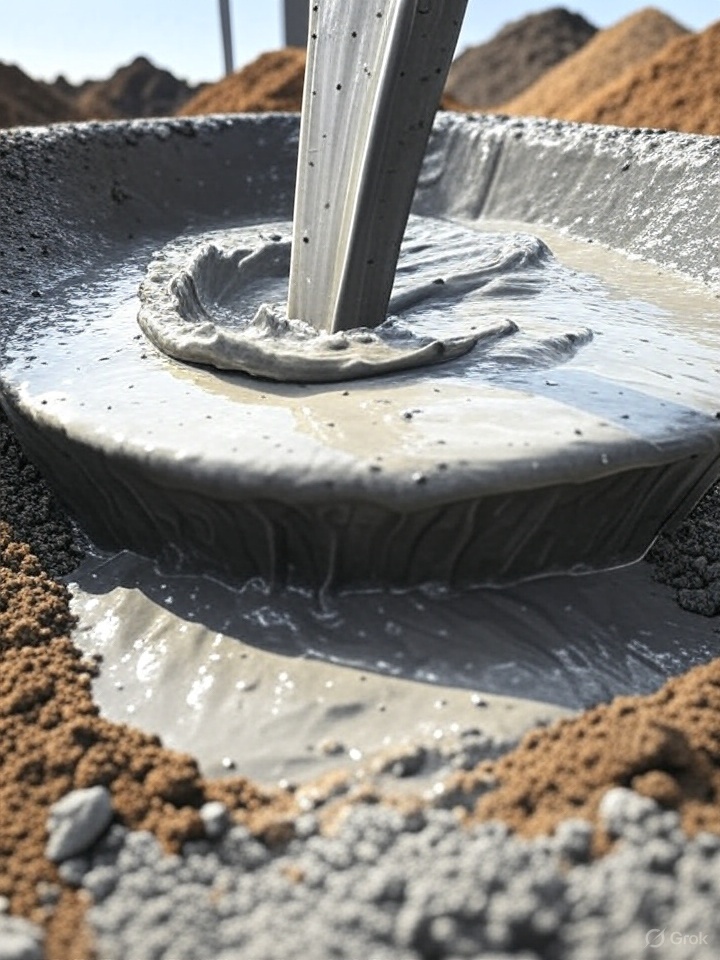

Unlocking the Power of Cement Slurry: Volume Concrete’s Versatile Solution for Modern Construction
Cement slurry, often referred to as neat cement, is a fundamental and versatile material in the construction industry, playing a critical role in ensuring the durability and stability of various projects. At Volume Concrete, we specialize in providing high-quality cement slurry tailored for specific applications, including cellular concrete production, grouting, and other innovative uses. This…
-
Detailed Analysis of Global Cement Production and Ownership
The global cement industry is a critical component of infrastructure development, with production and ownership structures reflecting economic, political, and environmental dynamics. This note provides a comprehensive analysis of who produces and owns cement worldwide, based on recent data and industry trends as of May 31, 2025. It expands on the key points and includes…
-

Geopolymer Cement Alternatives
Key Points Geopolymer cements are sustainable alternatives to traditional Portland cement, leveraging waste materials like fly ash and slag to create low-carbon binders. They show promise in reducing environmental impact and enhancing construction durability, but challenges like curing requirements and standardization need addressing. Environmental Benefits Geopolymer cements can cut CO2 emissions significantly, using industrial byproducts…
-

Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3) as a Next-Generation Solution
Concept: Limestone Calcined Clay Cement (LC3) combines limestone with calcined clay to create a low-carbon alternative to traditional Portland cement. It leverages limestone’s benefits while incorporating clay’s pozzolanic properties to further reduce clinker content and emissions. 2. Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU) with Limestone in Cement Concept: Limestone can be integrated into carbon capture and…
-
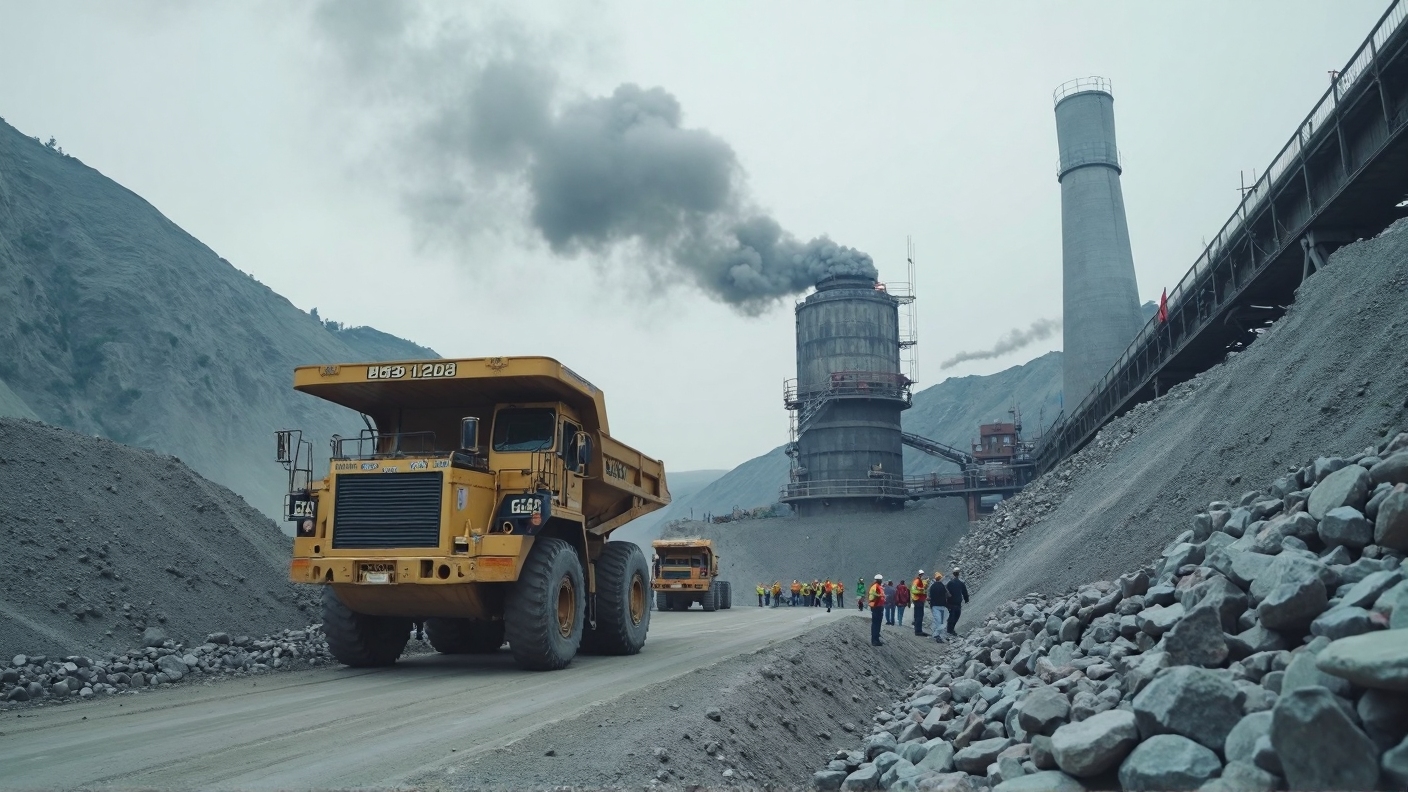

Limestone in Cement: A Cornerstone for Sustainability and Performance
Key Points Limestone plays a crucial role in cement, acting as both a primary ingredient and an additive that boosts sustainability. It provides the calcium needed for cement to bind materials together, forming the basis of concrete. Modern uses, like in Portland-Limestone Cement (PLC), show it can reduce environmental impact and improve cement qualities, making…
-

Air Entrainment in Concrete: Benefits, Challenges, and Practical Implications
Key Points Air Entrainment Benefits and Drawbacks Air entrainment involves adding tiny air bubbles to concrete, enhancing its resistance to freezing and thawing, which is crucial for cold climates. It also makes concrete easier to work with during pouring. However, it can lower the concrete’s strength, with each 1% air increase potentially reducing strength by…
-
Concrete Trivia
Concrete Trivia Challenge Test Your Knowledge: Concrete Trivia Challenge Score: 0/100 Next Question
-
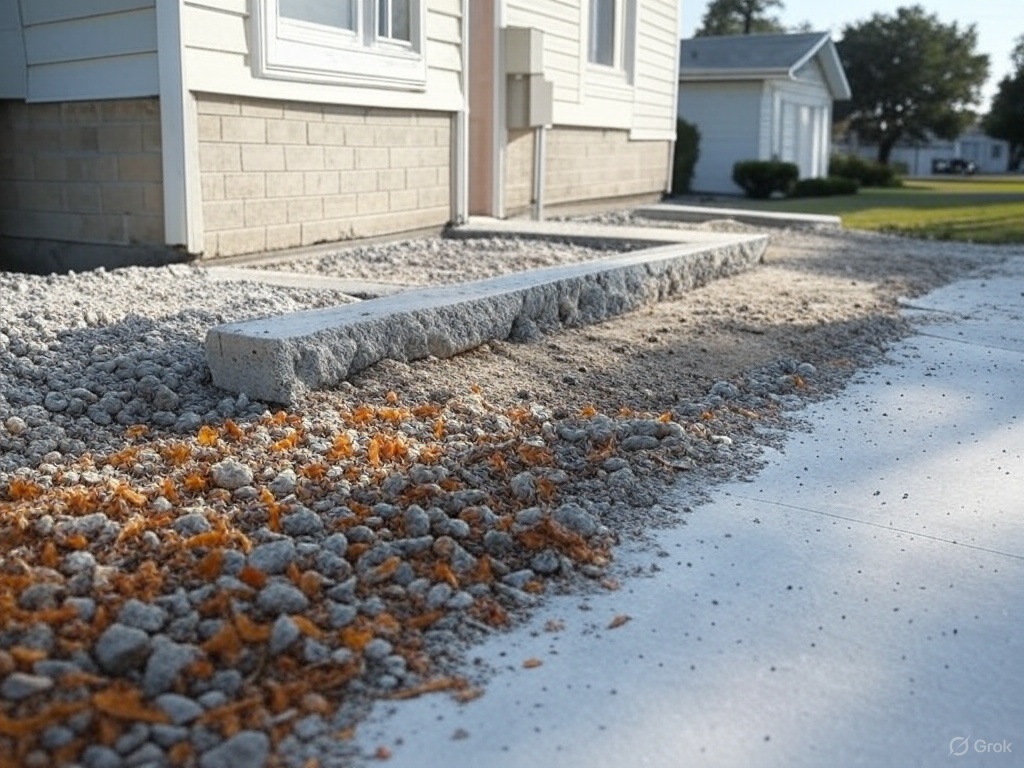

How LDCC Works for Insulation
Low-Density Cellular Concrete (LDCC) can be an effective material for foundation insulation, offering unique advantages due to its lightweight, thermal insulating properties, and versatility. Its effectiveness depends on factors like mix design, density, and the specific application, so let’s break it down: How LDCC Works for Insulation LDCC is a lightweight concrete made by mixing…
-
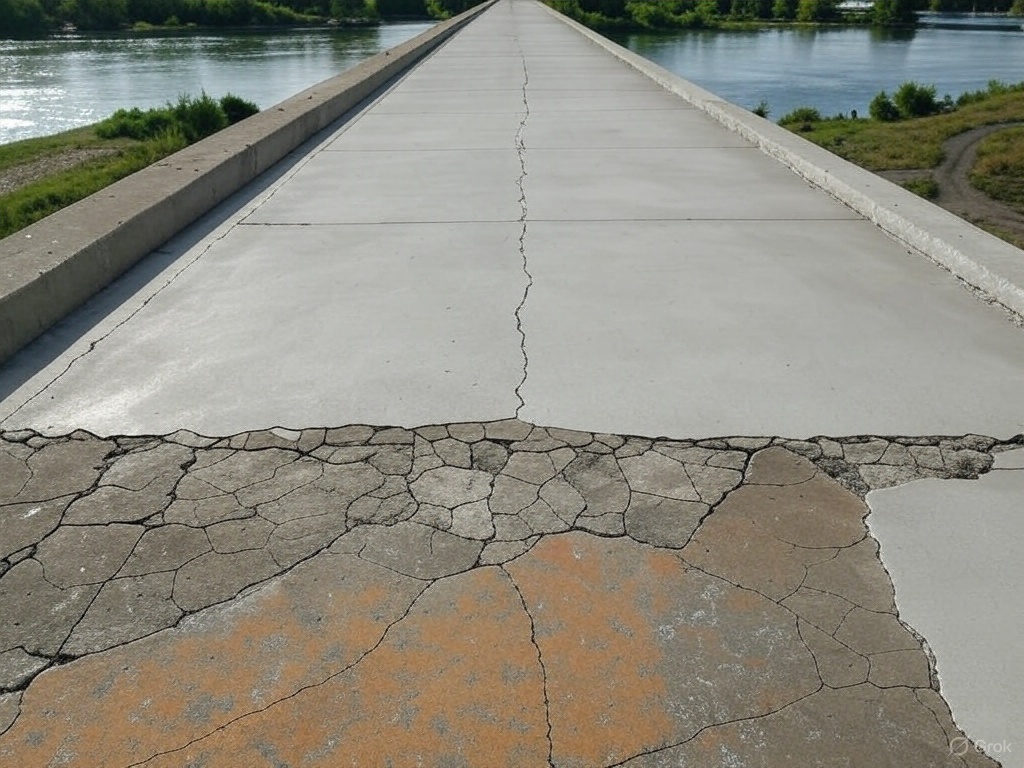

The Concrete That Fights Back: A Game-Changer or a Global Gamble?
The Concrete Revolution: Self-Healing Concrete That Could Save the World Imagine a world where crumbling bridges, cracking dams, and collapsing buildings are relics of the past. Enter self-healing concrete, a futuristic material straight out of science fiction that’s now breaking into reality—and it’s poised to revolutionize infrastructure on a dramatic scale. In March 2025, researchers…
-
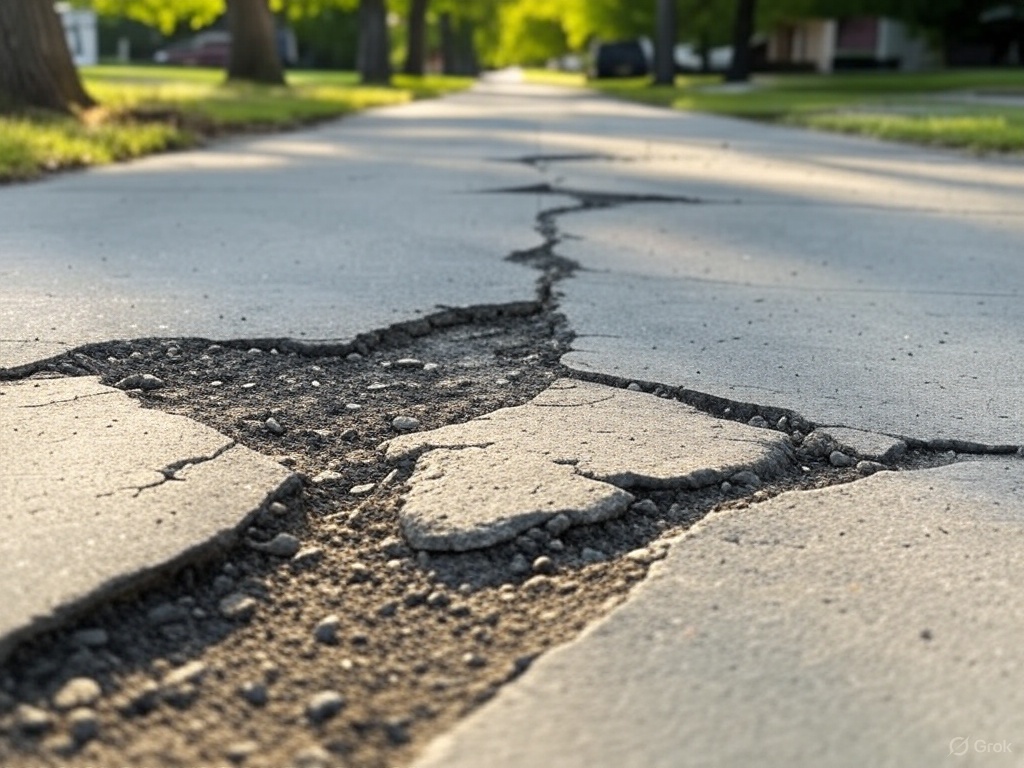

Understanding Alkali-Silica Reaction (ASR) in Concrete
Understanding Alkali-Silica Reaction (ASR) in Concrete Alkali-Silica Reaction (ASR) is a chemical reaction in concrete that can lead to significant deterioration, including cracking, expansion, and spalling. It occurs when the alkalis (primarily sodium and potassium) in the cement react with certain types of reactive silica found in aggregates, in the presence of moisture. This reaction…